Cyber Polygon 2021 concludes with discussions paving a path towards a greater centralization of power and surveillance that furthers the great reset agenda of the global economy and all societal structures.
The World Economic Forum (WEF) and partners’ annual Cyber Polygon cybersecurity training exercise concluded on July 9 with several key trends emerging that are likely to shape global policymaking for years to come.
These trends include:
- A desire to immunize the internet with digital antibodies to ‘protect’ society from cyberattacks and misinformation by exploiting ransomware attacks and a public health crisis to justify the centralization of power and control
- A demonization of cryptocurrencies in favor of central bank digital currencies where all transactions are recorded on a centralized ledger and have the ability to grant permissions on purchases, which further consolidates power
- A closer merger of corporation and state as the solution to any given crisis, be it cybersecurity, climate change, or COVID-19, without ever being put to a vote by the will of the people
Discussions coming out of Cyber Polygon 2021 concluded with the desire to immunize the internet, demonize cryptocurrencies, and prop-up centralized systems of governance through a closer merger of corporations and states (public-private partnerships).
The public-private solutions presented suggest that the WEF and partners are leading society down a path towards a greater centralization of power and surveillance that furthers the great reset agenda.
Here we take a deeper dive into the above trends emerging from Cyber Polygon 2021 while also showing how some of these agendas are already playing out on the world stage.
Immunizing the internet
Prior to the major ransomware attacks on critical infrastructures this year, the WEF released a short video on January 18, 2021 warning about a “cyber attack with COVID-like characteristics” that would “spread faster and further than any biological virus.”
The above video, which is now “unlisted” on YouTube, claims that COVID-19 was known as “an anticipated risk,” and so is its digital equivalent — a cyber pandemic.
Combating ransomware and other cyber threats is one way in which the WEF and partners are looking to immunize the internet from the fallout of a cyber pandemic.
“We need vaccines to immunize ourselves. The same is true for cyberattacks. Here, too, we have to move from simple protection to immunization. We need to build IT infrastructures that have digital antibodies built-in inherently to protect themselves” — Klaus Schwab, Cyber Polygon 2021
In his welcoming remarks at Cyber Polygon 2021, WEF Founder and Executive Chairman Klaus Schwab warned that a lack of cybersecurity had become “a clear and immediate danger to our society worldwide.”
Highlighting the recent ransomware attacks on critical infrastructures, Schwab likened cybersecurity to the coronavirus crisis in that both require immunization.
According to Schwab:
“We have to protect ourselves not only against the virus, we also have to develop the ability to withstand a virus attack.
“In other words, masks are not sufficient. We need vaccines to immunize ourselves.
“The same is true for cyberattacks. Here, too, we have to move from simple protection to immunization.
“We need to build IT infrastructures that have digital antibodies built-in inherently to protect themselves.”
But Schwab’s notion of digital immunity is nothing new.
“A war on cybercrime could easily become a war on Internet freedom” — World Economic Forum, 2012
In fact, the WEF has been talking about developing a digital immune systems for the internet for a decade.
According to one WEF report from 2012, “A war on cybercrime could easily become a war on Internet freedom,” and the solution could lie in “developing and disseminating countermeasures as threats emerge, or, in other words, building a digital immune system for the Internet.”
Immunizing the internet with digital antibodies, according to Schwab’s latest speech, requires public-private collaborations.
Where governments are limited in their knowledge and power, corporations can sweep in to fill the void.
According to Schwab, “Governments are in charge of guaranteeing security, but the deep expertise that is needed to develop a secure cyber ecosystem often lies with the private sector.”
“As long as you can hide behind cryptocurrencies, and as long as you’re pretty safe that you are not being caught, the price of running such attacks are pretty low. That’s one of the dynamics which we need to change together with governments” — Roger Halbheer, Cyber Polygon 2021
Speaking during the Cyber Polygon 2021 panel session called, “Digital state of tomorrow — what will it be?” Microsoft’s Chief Security Advisor Roger Halbheer said that ransomware attacks on critical infrastructure were a huge challenge, and that the public and private sector must work together to convict cybercriminals.
“Ransomware is a big issue, and really attacks on critical infrastructure are a huge challenge across the board,” said Halbheer.
“If you look at our intelligence at the beginning of the pandemic, it seems that certain underground groups agreed upon not attacking the healthcare sector with ransomware.
“I think this agreement lasted about two or three weeks because it’s just too tempting to attack them because you can make money,” he added.
The Microsoft exec then called for public and private collaborations to arrest and convict cybercriminals while taking aim at cryptocurrencies as being tools that need to be regulated.
“We have hooked so much stuff up to the internet now that you can create a much greater degree of disruption than you could, say, three or four years ago” — Michael Daniel, Cyber Polygon 2021
In a separate discussion, Michael Daniel, President and CEO of the Cyber Threat Alliance, told the panel on “Combating Ransomware” that he saw four ways in which the ransomware threat landscape has evolved:
- Ransomware is much more organized
- Ransomware is much more intense
- Ransomware is much more diverse
- Ransomware is much more disruptive
“One is that it is much more organized now. If your image of a hacker is someone in a hoodie still living in his mother’s basement, that’s not how the industry works now,” said Daniel.
“And it is an industry. It is highly organized and it’s very differentiating.”
Second, “It’s much more intense. We’re seeing a huge volume,” he added while backing up the claim that it’s much easier for cybercriminals to conduct ransomware attacks than ever before.
Third, “It’s much more diverse. The threat landscape — you can now attack not just laptops and phones, but you can attack devices, industrial control systems, a whole array of items.”
Fourth, “It’s much more disruptive. We have hooked so much stuff up to the internet now that you can create a much greater degree of disruption than you could, say, three or four years ago,” he added.
Daniel’s fourth point ties-back into what Klaus Schwab was talking about with the need to immunize IT infrastructure due to the fact that billions of home, office, industry, and mobile devices have already been connected to the internet.
A breach in one area of the internet can spell doom for the rest of the world and society as a whole, bringing down healthcare systems, water treatment facilities, transportation hubs, food supplies, and energy grids to name a few.
If the goal is to develop digital antibodies by eradicating ransomware, then getting rid of crypto and installing centralized digital currencies would be one ingredient in the globalists’ booster shot.
Demonizing crypto in favor of centralized digital currencies
The World Economic Forum and partners do not like decentralized cryptocurrencies. Instead, the unelected bureaucrats prefer the centralization and consolidation of power that Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) can provide.
Therefore, WEF members will take any opportunity to demonize decentralized cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
At Cyber Polygon 2021, the globalists took aim at the “Ransomware as a Service” business model as a means to target cryptocurrencies more broadly.
Teresa Walsh, Global Head of Intelligence FS-ISAC, told the Cyber Polygon 2021 panel on “Combating Ransomware” that ransomware would continue as long as cyber criminals were able to sit back and collect their Bitcoins, among other incentives.
“You can just go into the underground marketplace and purchase a kit, purchase a phishing kit to help you distribute it, and then just reap the benefits of the Bitcoins coming in as long as you give a little bit to the side to the operators behind the desk” — Teresa Walsh, Cyber Polygon 2021
“[Ransomware] is a service,” said Walsh, adding, “It’s a business model — the Ransomware as a Service — where you don’t have to be very knowledgeable yourself on how to create ransomware.
“You can just go into the underground marketplace and purchase a kit, purchase a phishing kit to help you distribute it, and then just reap the benefits of the Bitcoins coming in as long as you give a little bit to the side to the operators behind the desk.”
Walsh’s words echoed those of Microsoft Chief Security Advisor Roger Halbheer, who said in the “Digital State of Tomorrow” discussion:
“As long as you can hide behind cryptocurrencies, and as long as you’re pretty safe that you are not being caught, the price of running such attacks are pretty low.
“That’s one of the dynamics which we need to change together with governments.”
“Just imagine that you are able to give your kids some money in digital rubles and then restrict their use for purchase of junk food” — Alexey Zabotkin, Cyber Polygon 2021
Another Cyber Polygon 2021 discussion panel had a rather peculiar title: “New World — New Currency,” which elaborated on how central banks were looking to implement digital currencies where all transactions would be recorded on a single ledger.
The panel highlighted central bank efforts to roll out digital currencies that can be programmed with permissions on transactions, with the ability to restrict certain purchases.
“This [digital ruble] will permit better traceability of payments and money flow, and also explore the possibility of setting conditions on permitted terms of use of a given unit of currency” — Alexey Zabotkin, Cyber Polygon 2021
Bank of Russia Deputy Governor Alexey Zabotkin said that the digital ruble will “explore the possibility of setting conditions on permitted terms of use of a given unit of currency.”
“Just imagine that you are able to give your kids some money in digital rubles and then restrict their use for purchase of junk food,” he added.
So, to recap so far: immunizing the internet means eradicating ransomware and other threats, and part of eradicating ransomware means demonizing cryptocurrencies while pushing for fully centralized and permission-based Central Bank Digital Currencies.
Centralizing corporate & state power, surveillance, and control
Generally speaking, all proposed solutions lead towards giving public and private entities more power to surveil, control, coerce, and exert influence over all digital activity through the merger of corporations and states (public-private partnerships).
And with the WEF’s great reset agenda pushing for the merger of our physical, digital, and biological selves through the Internet of Bodies (IoB) ecosystem, what we are seeing is a future where the human body is physically connected to the internet at all times — thus making human beings themselves vulnerable to cyber attacks.
The IoB ecosystem is part of the Fourth Industrial Revolution that the World Economic Forum wishes to harness for its “great reset” agenda.
“After the Internet of Things, which transformed the way we live, travel and work by connecting everyday objects to the Internet, it’s now time for the Internet of Bodies,” wrote Xiao Liu, Fellow at the WEF’s Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
“This means collecting our physical data via devices that can be implanted, swallowed or simply worn, generating huge amounts of health-related information.”
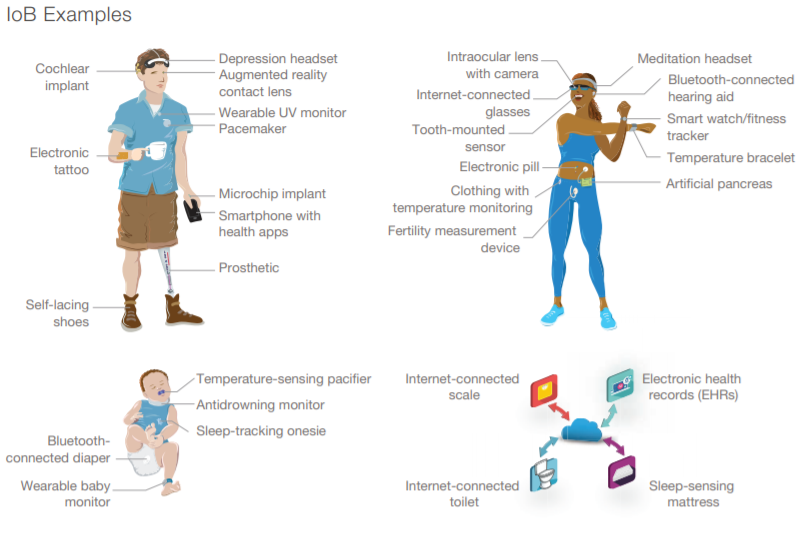
Internet of Bodies Examples, RAND Corporation
According to RAND, “Increased IoB adoption might also increase global geopolitical risks, because surveillance states can use IoB data to enforce authoritarian regimes.”
If and when the globalists’ technocratic utopia ever becomes reality, then a cyberattack on critical IT systems could bring the whole system down, sending the Internet of Bodies into chaos.
As human experiences are seemingly becoming more virtual on centralized systems, it would only make sense for the unelected globalist bureaucrats to make the internet as secure as possible.
After all, it would be a lot harder for them to track and trace all your activity online if they didn’t have total control over internet governance and regulations.
Today, we are seeing European countries like France mandating digital COVID health passes and vaccine passports for citizens to participate in “non-essential” daily activities such as going to restaurants and sporting events.
France will soon begin charging people for PCR tests as a means to coerce individuals into getting the vaccine and then signing up for the health passport, which threatens fundamental human rights on many levels, as previously reported on The Sociable.
But the technological means for greater control and surveillance don’t stop there.
Cyber Polygon 2020 and events playing out in 2021
At last year’s Cyber Polygon, Schwab warned of an inevitable cyber pandemic.
“We all know, but still pay insufficient attention to, the frightening scenario of a comprehensive cyber attack, which would bring a complete halt to the power supply, transportation, hospital services, our society as a whole” — Klaus Schwab, Cyber Polygon 2020
“We all know, but still pay insufficient attention to, the frightening scenario of a comprehensive cyber attack, which would bring a complete halt to the power supply, transportation, hospital services, our society as a whole,” Schwab said in 2020.
This year, the WEF founder followed-up on his “frightening scenario” by highlighting the recent ransomware attacks that have struck critical infrastructures around the world in 2021.
“Citizens are impacted by energy shortages, delayed medical treatment, and other effects this new breed of audacious cyberattacks causes” — Klaus Schwab, Cyber Polygon 2021
“We have seen in the past few months, for example, ransomware attacks targeting hospitals, critical infrastructure, school systems, the power grid, and many other essential services,” said Schwab.
“Citizens are impacted by energy shortages, delayed medical treatment, and other effects this new breed of audacious cyberattacks causes,” he added.
Ever prepping for an anticipated cyber pandemic, discussions from last year’s Cyber Polygon exercise centered around the globalists’ continued call for public-private collaborations, the adoption of digital identity schemes, and the desire to censor “misinformation” that went against authoritative messaging.
“Biden allied groups, including the Democratic National Committee, are also planning to engage fact-checkers more aggressively and work with SMS carriers to dispel misinformation about vaccines that is sent over social media and text messages” — Politico, 2021
Just this week, Politico reported that political organizations will engage “fact-checkers” to put pressure on SMS carriers to censor social media and text messages regarding vaccines.
According to Politico, “Biden allied groups, including the Democratic National Committee, are also planning to engage fact-checkers more aggressively and work with SMS carriers to dispel misinformation about vaccines that is sent over social media and text messages.”
Here we see politics making its way into the messaging policies of the private sector’s most influential platforms, despite the fact that White House spokesperson Kevin Munoz assured Politico that the administration was “committed to keeping politics out of the effort.”
“When we see deliberate efforts to spread misinformation, we view that as an impediment to the country’s public health and will not shy away from calling that out,” said Munoz.
Digital ID for me is a very big part of the future… Inevitably, governments are going to move in this direction — absolutely, inevitably” — Tony Blair, Cyber Polygon 2020
On the digital identity front, Tony Blair said at last year’s Cyber Polygon, “Digital ID for me is a very big part of the future.”
“Inevitably, governments are going to move in this direction — absolutely, inevitably,” he added.
Fast-forward to today and the health passes and vaccine passports are just stepping stones towards digital identity adoption.
For those unfamiliar, digital identities keep a record of all of your online activity, such as the websites you visit, who you communicate with, your health status, your financial information, credit score, etc.
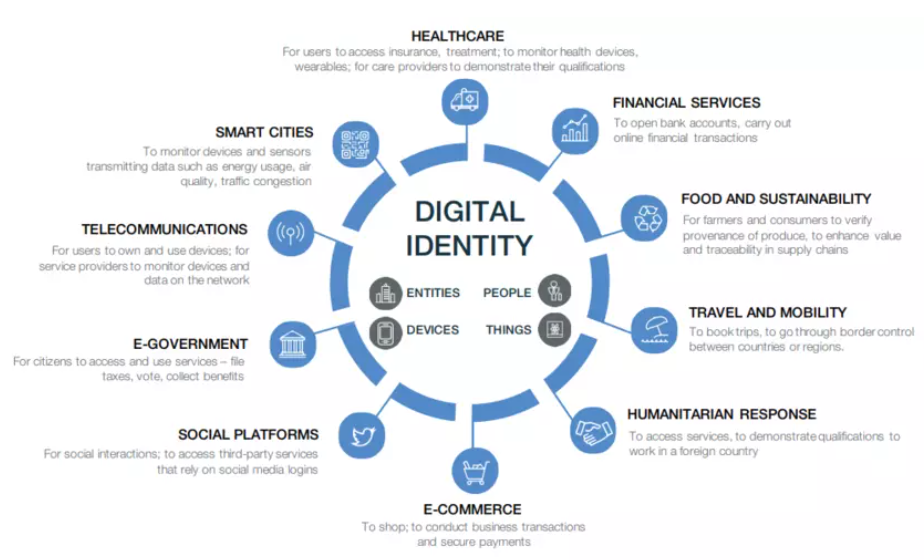
Image Source: World Economic Forum
According to a WEF report from 2018, “Our identity is, literally, who we are, and as the digital technologies of the Fourth Industrial Revolution advance, our identity is increasingly digital.”
“This digital identity determines what products, services and information we can access – or, conversely, what is closed off to us.”
In other words, digital identities — with health passports being just one component — are leading to a class system where people are given access to privileged information, products, and/or services based on the data recorded in their digital identities.
We are already seeing this play out with the vaccine passports, and it is unlikely to stop there.
The great reset agenda accelerates
The unelected globalists will take advantage of every crisis to exert their influence on politicians, business leaders, and civil society.
It doesn’t matter if the crisis has to do with cybersecurity, climate change, poverty, or a global pandemic — every solution the WEF puts forward calls for public-private collaborations — a closer merger of corporation and state.
The great reset agenda is a means to an end.
The end is centralized power and control over society through social and economic pressure that is enforced by Fourth Industrial Revolution technologies that power the Internet of Bodies, transhumanism, digital identities, global finance, food supply chains, and much more.
With Cyber Polygon 2021, we see the WEF and partners aiming to immunize the internet, demonize cryptocurrencies, and supersize their centralization of power without ever once putting their agenda to a vote by the will of the people.
A timeline of the great reset agenda: from foundation to Event 201 and the pandemic of 2020
Your digital identity can be used against you in the event of a great reset